Forge Training
Description
This course and the related material are designed to provide a working knowledge of the metal forging industry. The course is intended for the Mechanical Engineer or CAD designer with the intention to develop the forged part for the forging manufacturing process from the prototype. Forging is the process by which metal is heated and is shaped by plastic deformation by suitably applying compression force. This is an introduction to Forging Design using Creo or SolidWorks where the focus is on advanced modeling techniques where making changes is paramount. The class is intended for those designers and engineers who are designing forged parts using 3D parametric modelers such as SolidWorks or Creo. The bulk of the time will be spent on the part design requirements imposed on the design engineer by the forging process. Topics covered will include the approach to modeling forgings, and learning techniques where designers take a weldment and convert that assembly into a forged This training course is developed for seasoned users, who want to become proficient in learning forging part design and making changes quickly, setting one up to become an expert faster.
Topics:

- Overview of the forging process complete with tooling and outside machining operations
- History of Forging
- The progression of a forging process
- Metallurgy, Materials, and various alloys
- Open die drop hammer forging
- Impression die drop hammer forging
- Press forging, upset forging, automatic hot forging, and roll forging
- Powder mixes for compacting plus alloyed powder composed of two or more elements
- Use Parameters & Relations or Global variables & Equations with underlying curve geometry to drive Creo or Solidworks geometry with respect to forged parts
- Learn to use Solidworks or Creo surfacing, and discuss the necessity of forged part design with 20+ examples
- interrogate various forged parts in CAD to determine the auxiliary parting plane. Learn how to convert R&D models to the forged process.
- Techniques for converting multiple parts from a weldment into a cheaper, stronger forged part
- Convert Forgings for the machining process
- Document control GD&T on forged and their machined counterparts if applicable
- Terms and Definitions
Duration & Cost
16 hours = $1650 or 40 hours = $2850 per student
For corporate rates, please call (312)226-8339
Prerequisites
General knowledge of SolidWorks, Creo or another parametric 3D CAD modeler imperative unless you are in purchasing
Projects Creo or SOLIDWORKS
- Intense Draft exercise including alternate techniques for obtaining proper draft with respect to the forging process
- Production of Steel Forged rings
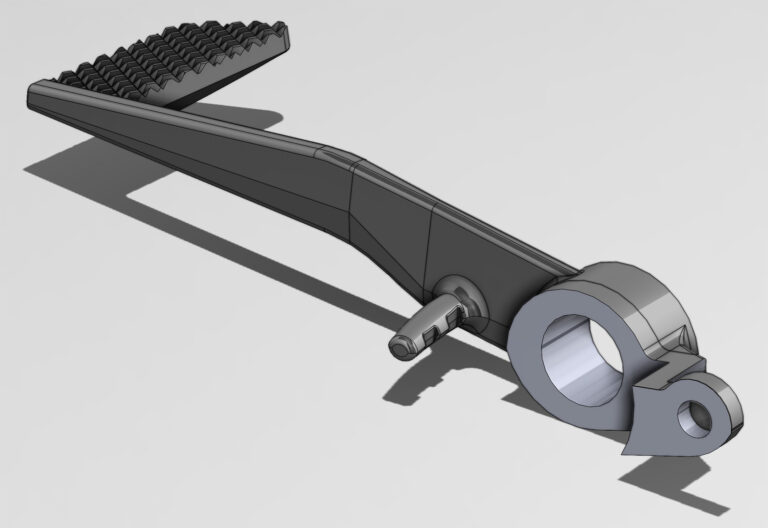
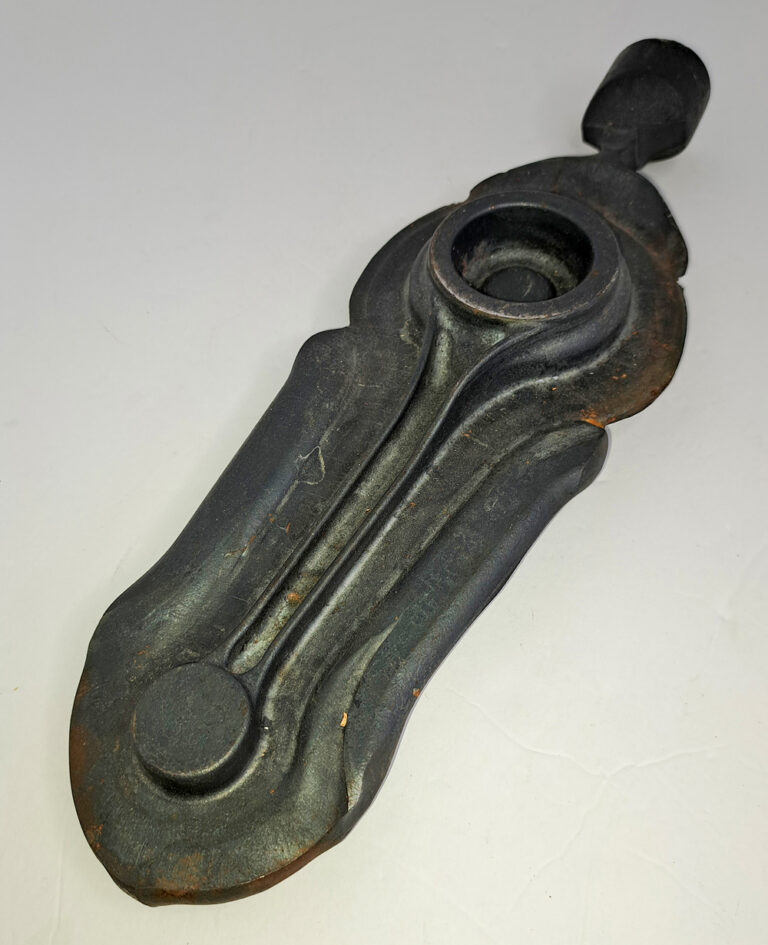
- Production of Motorcycle brake Lever
- Production Riffle upper & Lower forgings
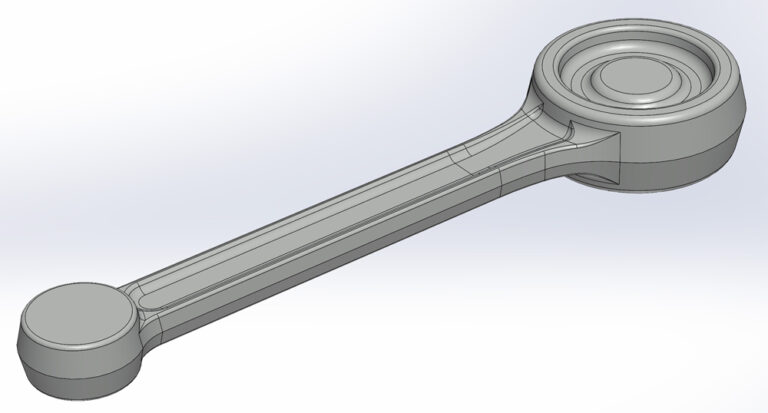
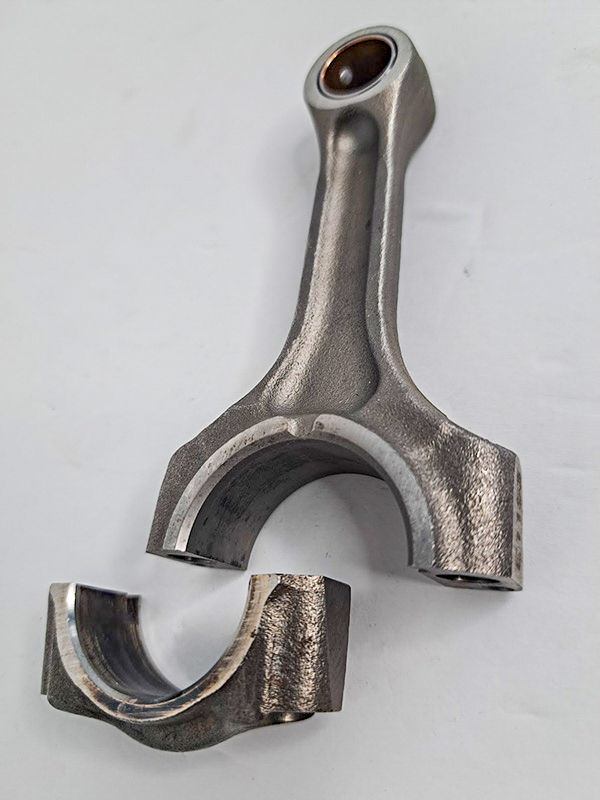
- Production of forged Harley-Davidson Rod
- Suzuki forged Piston
- Motorcycle footpegs
- Shears and other cutting tools
- Motorcycle Kickstand: Convert from a weldment to a forging model
- Convert welded assemblies complete with complex draft to a forged process
- Use Soldiworks or Creo to create the forging tool
- Compare metal injection molding, powder injection molding, and forging
Discussions

- Discuss the history of forming metals
- Advantages and disadvantages with respect to cost and strength
- Discuss various alloys with respect to forging
- Compare cold forging, hot forging, and warm forging
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of outsourcing
- Discuss basic design elements for forged part design, i.e. holes, ribs, thin wall features, bosses, nominal walls, and fill
- Discuss general rules for forging and how materials deform so designers can leverage the flow of material for strength
- Aircraft quality for high-stress forged parts
- Discuss auxiliary operations such as specific surface conditions or shapes, not obtained by the regular processing operations
- Flow stress with respect to deformation
- Discuss heat treatment
- Discuss ribs and the addition of fixture or gauge geometry for aligning for the CNC matching process forge part
- Discuss Draft requirements with respect to material flow
- Discuss specification, purchasing quantities, tooling, cost reduction, and cost of materials
- Discuss making parts ready for the forging process from R&D that others created i.e. technique, Draft, strike direction
- Discuss tips, tricks, and techniques for starting and completing forging parts using Creo or Solidworks
- Learn to utilize Draft Check analysis tools correctly
- Compare flow simulation utilities for estimating preforms and progressive die applications
- Discuss chrome applications and another electroplating, painting, or powder-coating processes
Video Training Delivery System
Ask your Design Engine account manager about our Training Delivery System(TDS), an easy-to-follow guide for designers and engineers who want a supplement to this course.
