Everyone keeping up with technology, engineering, and design should have heard about 3D printing. Much of the general population has heard of it, but most likely the majority don’t understand the capabilities and how this will change numerous industries, and supply chains. Before 3D printing people were predominantly using CNC machining to have the products made for them from designs specifications in data files. However, these machines cost big money, are heavy, and take up large amounts of space. Though it sounds cliche, 3D printing is a game changer.
Also referred to as additive manufacturing, 3D printed products are made by adding layers on top of each other,early on the most commonly used materials were plastic, but ceramics, concrete and metal are increasingly being used. Depending on various factors such as needs, capabilities, and features, a 3D printer can be purchased for a few hundred dollars for something small you would assemble use at home, to thousands of dollars for something more industrial.
CAD — Design Software for 3D printing
Besides the printer itself, one would need CAD software. Individuals create a design in the software, then the 3D software would read the file data, and create the item based on the design specifications. A few common modelling software with excellent design capabilities are:
- TinkerCAD
- SketchUp
- SolidWorks
- Rhino3D
- Maya
- Creo
- Fusion360
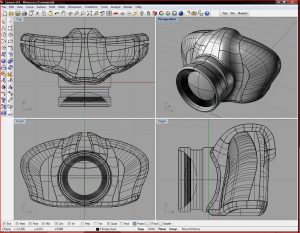
One place were 3D printing will have a significant effect on is the spare-parts industry. Increasingly manufacturers are using this form of additive manufacturing to produce parts for items ranging from automotive, electronics, to aerospace. GE is now incorporating this method for producing jet nozzles (pictured below). Before they started printing this unit themselves, they sourced parts to make this from 18 different vendors.
With the snowballing rate of 3D printed parts coming into the market, Forbes expects the spare parts supply chain will shift in the direction 3D printed solutions within the next 3 years. An analysis by Strategy& states “ 85 percent of the spare parts providers assert that 3D printing will also play a dominant role in the spare parts business”. The ability to print spare parts will decrease companies inventory holding space needs, and make it possible to make parts as they are ordered. With decreased holding costs, increased speeds, comes decreased costs. A study says in 10 years, German spare parts suppliers will save €3 billion a year by implementing 3D printing (strategy&).Now companies such as Kazzata have sprouted as a spare parts digital supply chain.
Companies are currently implementing 3D printing of production spare parts and they are changing the way they do business due to additive manufacturing advancements, and cost savings. Stategy& states that 50% of customers are looking into 3D printing replacement parts. Themselves. Automobile manufacturers such as Mitsubishi, Mercedes, and Ford have made investments in 3D printing solutions. These companies are currently printing spare parts for their older vehicles.
3D printing increased efficiency and cut costs and complexity. It is a tool for large companies and manufactures, and a tool that empowered the common man that has a computer, CAD software and design skills. Maybe when the part for our old items are no longer produced, we will just simply make ourselves at home. It will be fascinating seeing what the future brings thanks to this technology.
(CAD education available with Design Engine. Training information available at proetools.com )
Written by Eli Petrov